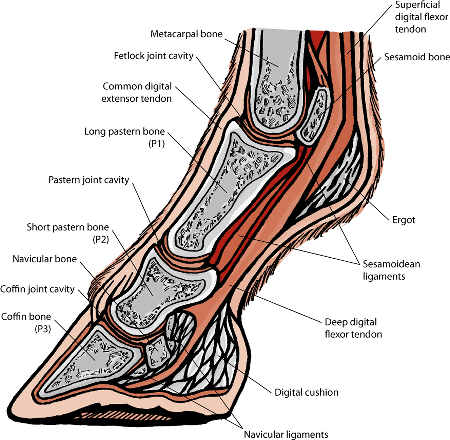
“Navicular” is a dreaded word. It is often not discussed unless the conversation addresses navicular syndrome or another disheartening hoof ailment. While navicular syndrome may be frightening, the navicular bone is a good thing! I’d like to give the navicular bone the spotlight and some love by expressing its notable functions and physiology.
The navicular sesamoidean bone resides approximately at the level of the coffin joint, posterior or behind the coffin bone and short pastern, and anterior to the digital cushion. The coffin bone connects to the navicular by the impar ligaments. The navicular bone is also secured by the collateral sesamoidean ligament, which attaches to the short pastern. The navicular bone is called so because of its canoe-like shape (“navicu” in Latin meaning “small boat”). This canoe-like structure has an accessory titled the navicular bursa. This cartilaginous sac cradles the caudal navicular bone and allows the deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT) to glide smoothly along its surface. This is the simple, primary function of the navicular bone – to provide a surface for the DDFT to smoothly swivel across as it continues onto its connecting point at the coffin bone.
On the other hand, a navicular “diagnoses” can be devastating. Navicular syndrome is a deep unknown. The specific of what causes caudal heel pain is a general understanding, not a science, and there is much education yet to be discovered. Horses with poor hoof conformation due to inadequate shoeing or improper trimming are the most common causalities of navicular syndrome, although conformational defects from genetic principle plays a role, as well. Poor hoof conformation, such as underrun and/or contracted heels, leads to additional stress being placed on the DDFT, extra pressure on the navicular bone, and a degeneration of the digital cushion which is a shock absorber for the internal structures of the lower limb. Without a healthy digital cushion, impact with the ground forces a blow to the navicular area causing trauma over time. Another trauma source is horses with excessively high heels and upright pasterns, which place pressure and stress in unnatural ways on the DDFT and navicular. Poor blood flow into or out of the navicular may also be responsible for pressure build-up and mineralization or degeneration of the bone structure. Obstruction of vascular function can be caused by a weak digital cushion or unsuitable heel disposition (i.e. high or underrun). As you can imagine, degeneration or over-calcification of the navicular bone, in turn, inflicts strain and distress on the DDFT.
Proper trimming methods and stimulation of the heel are ways to encourage navicular syndrome rehabilitation. For more severe cases, injections or surgery may be necessitated. It’s important to consult with your veterinarian and hoof care practitioner to determine a treatment plan. EasyCare is available to help make the rehabilitation process less complex for you and your horse. The Easyboot Rx is an excellent boot option for concussion absorption while still promoting circulation. Contact EasyCare today to find a hoof boot option to help you and you horse achieve optimal equine health and performance.
Mariah Reeves

Customer Service
As one of the customer service representatives, I am happy to help get your horse into the right boots. I promote holistic methods of equine care and will assist you with finding the perfect fit for horse and rider.